When taking your pet to the hospital, doctors often recommend that your pet have an ultrasound, DR, CT, MRI …… However, many pet owners do not understand the role of these imaging instruments, and imaging programs are all high-cost, and the lack of information between the pet owner and the doctor can easily lead to the pet owner’s distrust of the doctor, exacerbate the deterioration of the doctor-patient relationship, and ultimately have an impact on the pet’s disease. Below is an overview of the differences between animal ultrasound, DR, CT, and MRI imaging programs.
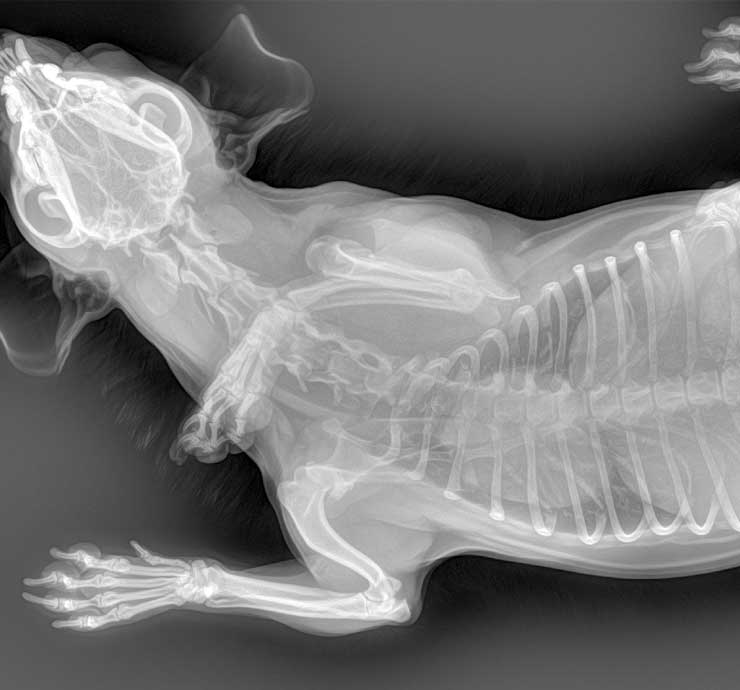
Veterinary DR
Often referred to as Veterinary X-ray equipment, is currently the most frequent use of imaging equipment. DR needs to be set up in a separate room, and need to stay away from residential buildings. Principle of work: the application of x-ray penetrating ability, fluorescence and light-sensitive role, after penetrating the animal body so that a variety of structures in the fluorescent screen or film images, the scope of the examination involves all parts of the body of the animal. x-ray examination can only provide two-dimensional plane image, imaging is susceptible to the impact of thick hair, too thick soft tissue, so generally used as a preliminary examination. x-ray has a slight radiation, but according to scientific research, the amount of radiation received by taking an x-ray film. However, according to scientific research, the amount of radiation received from an X-ray is well within safe limits. However, for insurance purposes, it is not recommended that pregnant women or expectant parents enter the DR room to assist in bonding their pets during an X-ray examination to avoid harming the fetus. The person who assists in the boding needs to wear special protective clothing to protect the vital organs of the body from the effects of radiation. The anti-radiation clothing is a heavy lead suit, and for cats that undergo DR examination for the purpose of checking the number of fetuses, the amount of radiation they receive is also within the safe value, so there is no need to talk about radiation.
Compared to several other imaging devices, the results of DR are relatively straightforward, and the approximate shape of a bone can be seen on the film even without basic medical knowledge. Animal X-rays and animal ultrasounds are complementary. Chest X-rays can easily show an enlarged heart, while echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart) examines the different chambers of the heart and provides an accurate and quantitative assessment of heart disease.
Animal ultrasound
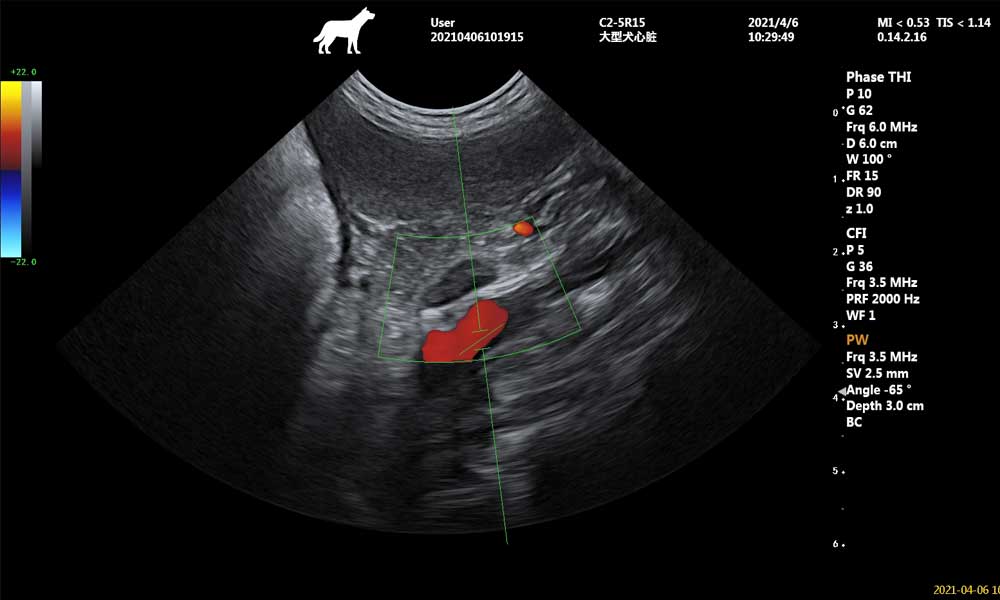
This is the use of ultrasound technology for imaging. Ultrasound refers to high-frequency sound waves that cannot be heard by the human ear. It can be heard up to 20,000 kHz, and diagnostic ultrasound has a frequency between 2 and 15 MHz. Principle of operation: In diagnostic ultrasound, the ultrasound pulse enters the muscle, sweeps through the tissue until it meets a reflective interface and returns to the transducer, which also acts as a receiver. The returned signal is called an echo, which is processed by a computer and displayed on the screen as a two-dimensional image. Doctors often request ultrasound: B/W ultrasound, color Doppler ultrasound (color ultrasound.) B ultrasound is a two-dimensional image, mainly used to determine the presence or absence of the affected area of the swelling, foreign body, inflammation, fluid, calcification, fibrosis, gas and so on. Color ultrasound is a three- (four-) dimensional image that can detect the speed and direction of blood through Doppler ultrasound, and is mostly used to determine blood flow within the cardiovascular system, which is an irreplaceable function of color ultrasound compared to other imaging tests, and has an indispensable role in the diagnosis of heart disease.
A veterinary ultrasound system equipment supporting ultrasound and color ultrasound functions
During the ultrasound examination, the pet needs to remain motionless, and the examination takes longer than the DR, usually about 5-10 minutes for one part, and even longer for the heart part. There is no need for additional sedation if the pet owner assists in calming the pet effectively. This non-invasive, flexible and relatively safe technique is becoming more widely used in clinical practice.
In addition, animal ultrasound examinations require shaving of the examination site to avoid the influence of hair on the ultrasound conduction of the probe. At the same time, a coupling agent is applied to increase conduction and lubrication, and at the end of the examination, it is wiped off with a paper towel or can be wiped off with a hot towel, and pets are kept from licking and cleaning as much as possible.
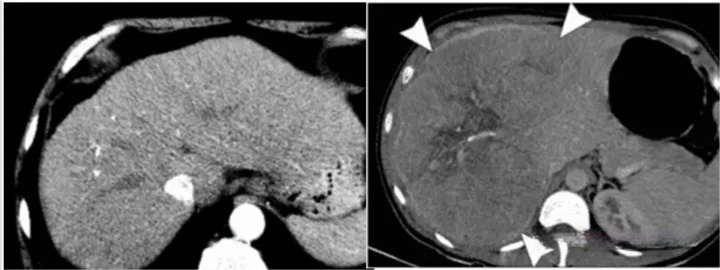
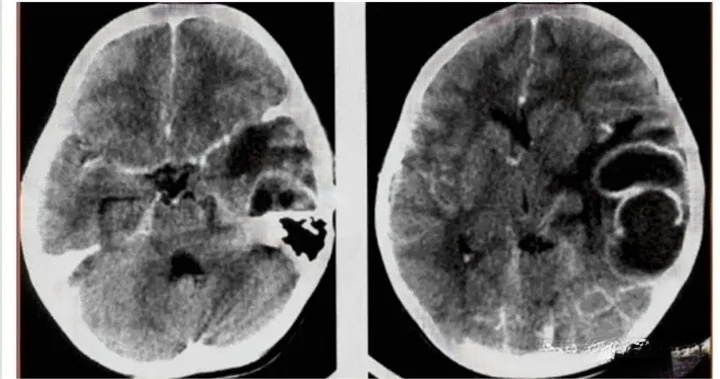
CT
That is, X-ray computed tomography, is another leap forward on the basis of X-ray imaging, is an important milestone in the history of the development of radiology. Working Principle: The basic principle of CT imaging is to use X-ray beams to scan a certain thickness of the level of the animal inspection site, by the detector to receive X-rays through the level of the visible light, converted to electrical signals by the photoelectric converter, and then by the analog-to-digital converter to digital signals, input computer for complex processing, and finally into the form of an image.
Simply put, CT is equivalent to a dynamic all-round DR, but its diagnostic role is far greater than the basic DR. CT examination of intracranial tumors, abscesses and granulomas, parasitic diseases, traumatic hematomas and brain injury, cerebral infarction and cerebral hemorrhage, as well as intravertebral canal tumors and intervertebral disc prolapse and other diseases of the diagnostic effect of the diagnosis of the better, more reliable diagnosis.
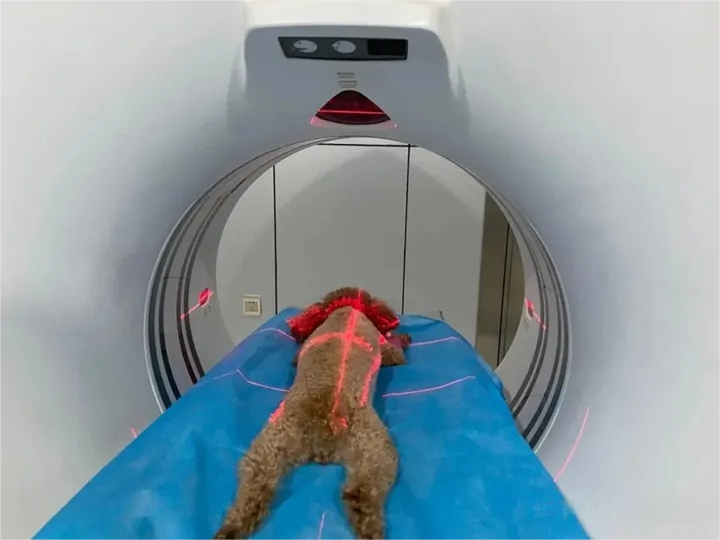
The use of CT equipment requires a high level of hospitals, due to the constant emission of radiation during the work, the equipment must be far away from residential housing, and the need to establish a closed environment to prevent radiation.
When the machine is working, pets need to be anesthetized and kept still, otherwise the quality of the image will be affected, and pet parents are not allowed to enter the workroom to accompany (high radiation).
In addition, the cost of the examination is relatively high, usually more than 2k RMB, and does not include the cost of anesthesia.CT examination scanning a part of the time will not be particularly long, after the completion of the position of the start scanning to the end, usually about 10 minutes will be finished.
MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). This equipment does not produce radiation, but is often mistakenly thought to be harmful because of the name “MRI”. Principle of operation: Magnetic resonance imaging technology refers to the examination of the examined muscle in a strong magnetic field, which causes the hydrogen atoms in the muscle to be aligned in the direction of the magnetic field. The tissue within the magnetic field is subjected to short-term radio frequency pulses, which temporarily disrupts the atomic arrangement. When the atoms are rearranged again, the examined tissue emits a specific signal. A receiving coil placed in the examined area records the signals emitted by the tissue, and a computer processes the signals to give cross-sectional images at different levels and in different shades of gray. Because it works through a magnetic field, this equipment also requires a closed environment and no electronic devices or other objects that interfere with the magnetic field should be placed in the room. In addition, MRI takes a long time to work, at least 30 minutes from the time of positioning to the completion of a scan of a site, and in some cases additional enhanced scans are required, which take more time to work, and pets must be anesthetized, and usually breathing anesthesia, with an anesthesiologist coming into the workroom for anesthesia monitoring. MRIs are similar to CTs, cost around $2k and are generally not included in the cost of anesthesia.
It has excellent diagnostic capabilities for the brain, thyroid, liver, gallbladder, spleen, kidneys, pancreas, adrenal glands, uterus, ovaries, prostate and other parenchymal organs, as well as the heart and great vessels. Compared with other auxiliary means of examination, magnetic resonance has the advantages of multiple imaging parameters, fast scanning speed, high tissue resolution and clearer images, etc. It can help doctors “see” early lesions that are not easy to detect, and has become a powerful tool for the early screening of tumors, heart disease and cerebrovascular disease.
Through the above introduction of animal ultrasound, animal DR equipment, CT, MRI, these imaging equipment has its own advantages in clinical diagnosis, the pet doctor will choose the appropriate equipment for examination according to the specific circumstances.
Post time: Jan-25-2024